Unveiling the World of Forex Trading

Forex, the foreign exchange market, is the world’s largest financial market, with an astounding average daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion. It operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, facilitating currency trades across every time zone. Unlike stock markets, forex trading involves pairs, meaning you buy one currency while simultaneously selling another. This global marketplace is where banks, corporations, governments, and investors converge to exchange and speculate on currency fluctuations.
The allure of forex trading lies in its high liquidity, extensive trading hours, and the vast number of trading opportunities it presents. It’s a market driven by geopolitical events, economic indicators, and the global macroeconomic landscape, making it both challenging and potentially profitable for traders. Forex traders employ various strategies, from technical analysis to fundamental analysis, to predict currency movements and make trading decisions.
Currency values in the forex market are incredibly sensitive to global events, making news and economic data critical tools for traders. Interest rate decisions, unemployment figures, and political instability can all cause significant swings in currency values. As a result, forex trading requires not only a keen understanding of economic fundamentals but also an awareness of global events.
The forex market’s accessibility is another attractive feature. With the advent of online trading platforms, anyone with a computer and internet connection can trade currencies. This democratization of forex trading has opened up opportunities for retail investors, who now play a significant role in the market alongside major financial institutions.
However, the forex market’s volatility also introduces significant risks. Currency values can fluctuate wildly in response to events, leading to potential losses for traders. Risk management strategies, including the use of stop-loss orders and leverage limits, are crucial for navigating the forex market successfully.
In summary, forex trading offers vast opportunities but also comes with high risks. Understanding the market’s mechanics, staying informed about global events, and employing solid risk management strategies are essential for anyone looking to delve into the world of currency trading.
Exploring the Major Forex Currencies

The backbone of the forex market is the major currency pairs, which consist of the most traded currencies worldwide. These include the US Dollar (USD), Euro (EUR), Japanese Yen (JPY), British Pound (GBP), Australian Dollar (AUD), Canadian Dollar (CAD), Swiss Franc (CHF), and the New Zealand Dollar (NZD). The dominance of these currencies is attributed to their countries’ significant economic stature and stability.
The US Dollar stands out as the most dominant currency in the forex market, often referred to as the world’s reserve currency. It’s involved in approximately 88% of all currency trades. The Euro is the second most traded currency, playing a central role in the European Union’s economy. The Japanese Yen is renowned for its role in carry trade strategies, owing to Japan’s historically low-interest rates.
Pairs involving these major currencies, such as the EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and GBP/USD, are known for their liquidity and lower spreads. This makes them attractive to traders, from beginners to professionals, due to the abundance of trading opportunities they present and their relatively lower transaction costs.
However, trading these major pairs requires an understanding of the economic fundamentals that drive their values. Economic indicators, such as GDP growth rates, interest rate decisions, and employment data, significantly impact these currencies. Traders must stay informed about these indicators and how they can affect currency pairs.
In sum, the major forex currencies and their pairs are the foundation of the forex trading world. Their economic significance, coupled with high liquidity and stability, makes them a central focus for traders aiming to capitalize on currency fluctuations in the global market.
Diving into Exotic and Minor Pairs
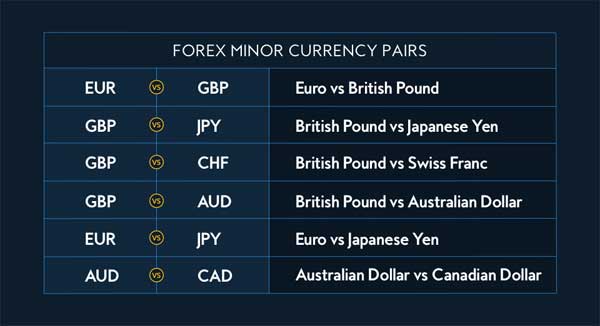
Beyond the major pairs lie the exotic and minor pairs, offering traders a different set of opportunities and risks. Minor pairs, also known as cross currency pairs, do not include the US Dollar. Examples include the EUR/GBP, AUD/NZD, and EUR/JPY. These pairs are less liquid than the major pairs but can offer more significant opportunities for returns due to their higher volatility.
Exotic pairs involve one major currency and a currency from a developing economy, such as the USD/SGD (Singapore Dollar), USD/HKD (Hong Kong Dollar), or EUR/TRY (Turkish Lira). These pairs are characterized by their low liquidity and high spreads, making them riskier but potentially more profitable.
Trading exotic and minor pairs requires a deep understanding of the economic and political conditions in the involved countries. Exotic currencies, in particular, can be susceptible to rapid and unpredictable movements due to political instability or economic events in the developing country.
Despite their risks, exotic and minor pairs can be attractive to traders looking to diversify their portfolios. They offer exposure to different markets and economies, potentially opening up new trading strategies and opportunities.
However, traders should approach these pairs with caution. The high volatility and low liquidity can lead to significant losses, especially without proper risk management. Understanding the unique factors that drive these currencies is crucial for anyone looking to trade exotic or minor pairs.
In conclusion, exotic and minor pairs expand the horizons of forex trading, providing access to a broader range of currencies and markets. While they come with increased risks, they also offer the potential for substantial rewards for well-informed and cautious traders.
The Dynamics of Currency Pair Correlations
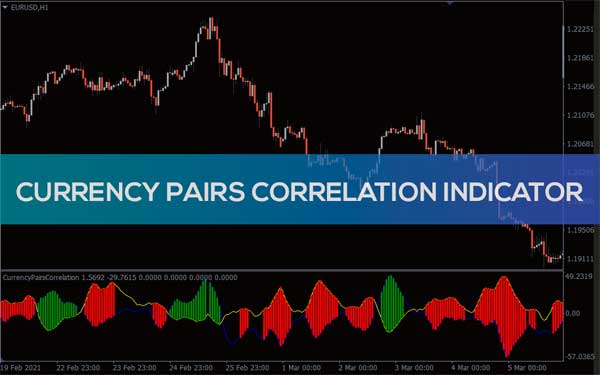
Forex markets are an intricate web of correlations, where the movement of one currency pair can affect another. Understanding these correlations is crucial for managing risks and strategizing trades. Currency pairs can be positively correlated, moving in the same direction, or negatively correlated, moving in opposite directions.
For example, the EUR/USD and GBP/USD pairs often move in tandem because both currencies tend to react similarly to US Dollar movements and economic events. On the other hand, the AUD/USD and USD/CAD often move in opposite directions due to their countries’ differing economic health and commodity exports.
Traders can use these correlations to hedge their positions, reducing risk by taking opposite positions in correlated pairs. However, correlations can change over time due to shifts in economic policies, interest rates, and geopolitical events. Constant monitoring and analysis are therefore essential.
Understanding correlations also allows traders to avoid overexposure to a single currency. By recognizing how pairs are related, traders can spread their risk more effectively across different currencies and markets.
However, relying solely on correlations can be risky. Unforeseen events or changes in market sentiment can disrupt established patterns, leading to potential losses. As such, correlations should be one of many tools in a trader’s arsenal, used alongside other forms of analysis and risk management techniques.
In summary, the dynamics of currency pair correlations offer valuable insights for forex traders. By understanding and utilizing these relationships, traders can enhance their strategies, manage risk more effectively, and potentially increase their chances of success in the volatile forex market.
Strategies for Navigating Forex Market Volatility

Forex market volatility can be both a blessing and a curse for traders. On one hand, it presents opportunities for substantial profits; on the other, it carries the risk of significant losses. Developing strategies to navigate this volatility is crucial for any forex trader’s success.
One fundamental strategy is the use of stop-loss orders. These orders automatically close out a position at a predetermined price, limiting potential losses. Traders can also use take-profit orders to lock in gains before the market potentially moves against them.
Diversification is another key strategy. By spreading investments across various currency pairs, including majors, minors, and exotics, traders can reduce their exposure to the volatility of any single currency or market event.
Leverage can amplify profits in forex trading, but it also increases risk. Using leverage cautiously, or opting for lower leverage ratios, can help manage the risks associated with market volatility.
Technical and fundamental analysis are also vital tools. Technical analysis involves studying price charts and patterns to predict future movements, while fundamental analysis looks at economic indicators and news events. Both can provide insights into market trends and help inform trading decisions.
Finally, keeping abreast of geopolitical and economic news is essential. Events like elections, policy changes, and economic reports can trigger volatility. Staying informed allows traders to anticipate market movements and adjust their strategies accordingly.
In essence, navigating forex market volatility requires a blend of careful planning, risk management, and ongoing education. Traders who master these strategies can potentially harness volatility for their gain, rather than falling victim to it.
Deciphering Forex Trends: A Trader’s Guide

Understanding and identifying trends is central to successful forex trading. A trend represents a general direction in which a currency pair is moving. Traders can use trend analysis to make more informed decisions, whether they’re planning to enter a long position in an uptrend or a short position in a downtrend.
There are three main types of trends: uptrends, downtrends, and sideways trends. An uptrend is characterized by higher highs and higher lows, indicating that the currency pair’s value is increasing. Conversely, a downtrend is marked by lower lows and lower highs, signaling a decrease in value. Sideways trends, or range-bound markets, occur when there’s little movement up or down, and the prices fluctuate within a narrow range.
Technical indicators are invaluable tools for trend analysis. Moving averages, for example, can help smooth out price data over a specified period, making it easier to identify the underlying trend. The Relative Strength Index (RSI) and MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) are other popular indicators that can signal trend strength and potential reversals.
Chart patterns, such as triangles, head and shoulders, and flags, can also provide insights into future market movements. Recognizing these patterns and understanding what they signify can help traders forecast where the market is headed next.
However, it’s important to remember that trends can change due to various factors, including economic events, political instability, and changes in market sentiment. Therefore, traders should always be prepared to adjust their strategies in response to new information.
In conclusion, trend analysis is a fundamental aspect of forex trading. By understanding and identifying market trends, traders can make more informed decisions, manage risks more effectively, and increase their chances of success in the forex market.
Comparison Table: Major, Minor, and Exotic Currency Pairs
| Pair Type | Characteristics | Liquidity | Volatility | Spread |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Majors | Involves USD and another major currency | High | Lower | Narrow |
| Minors | Does not involve USD | Moderate | Moderate | Wider than majors |
| Exotics | One major currency and one from a developing economy | Low | High | Widest |
This table highlights the key differences between the major, minor, and exotic currency pairs, providing a quick overview for traders to understand their options in the forex market.






Forex trading is the world biggest financial market. It trades over $6 trillion daily.
Exotic and minor pairs are more volatile and riskier but can be very profitable.
Forex operates 24 hours a day, five days a week. It involves trading currency pairs.
Forex market has high liquidity and a lot of trading opportunities.
Anyone with internet can trade currencies now. This is great for retail investors.
Major currency pairs like USD/EUR and USD/JPY have high liquidity and lower spreads.
Forex trading can be risky. Using stop-loss orders and managing risks is important.
Currency values in forex are very sensitive to global events and news.